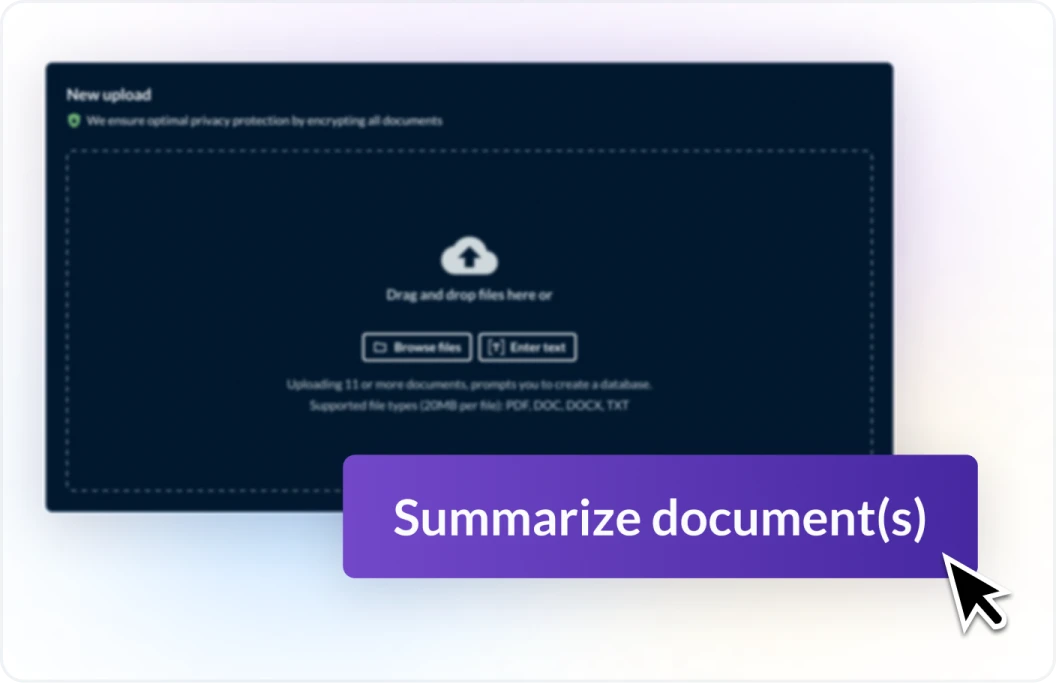
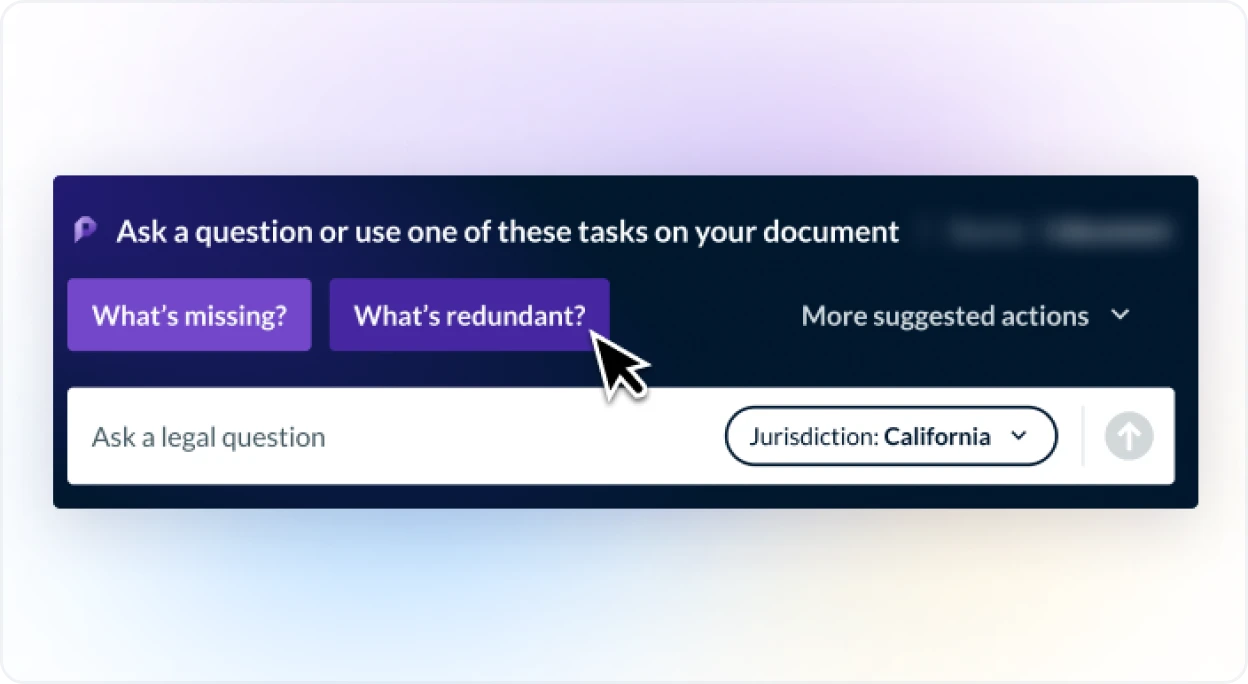
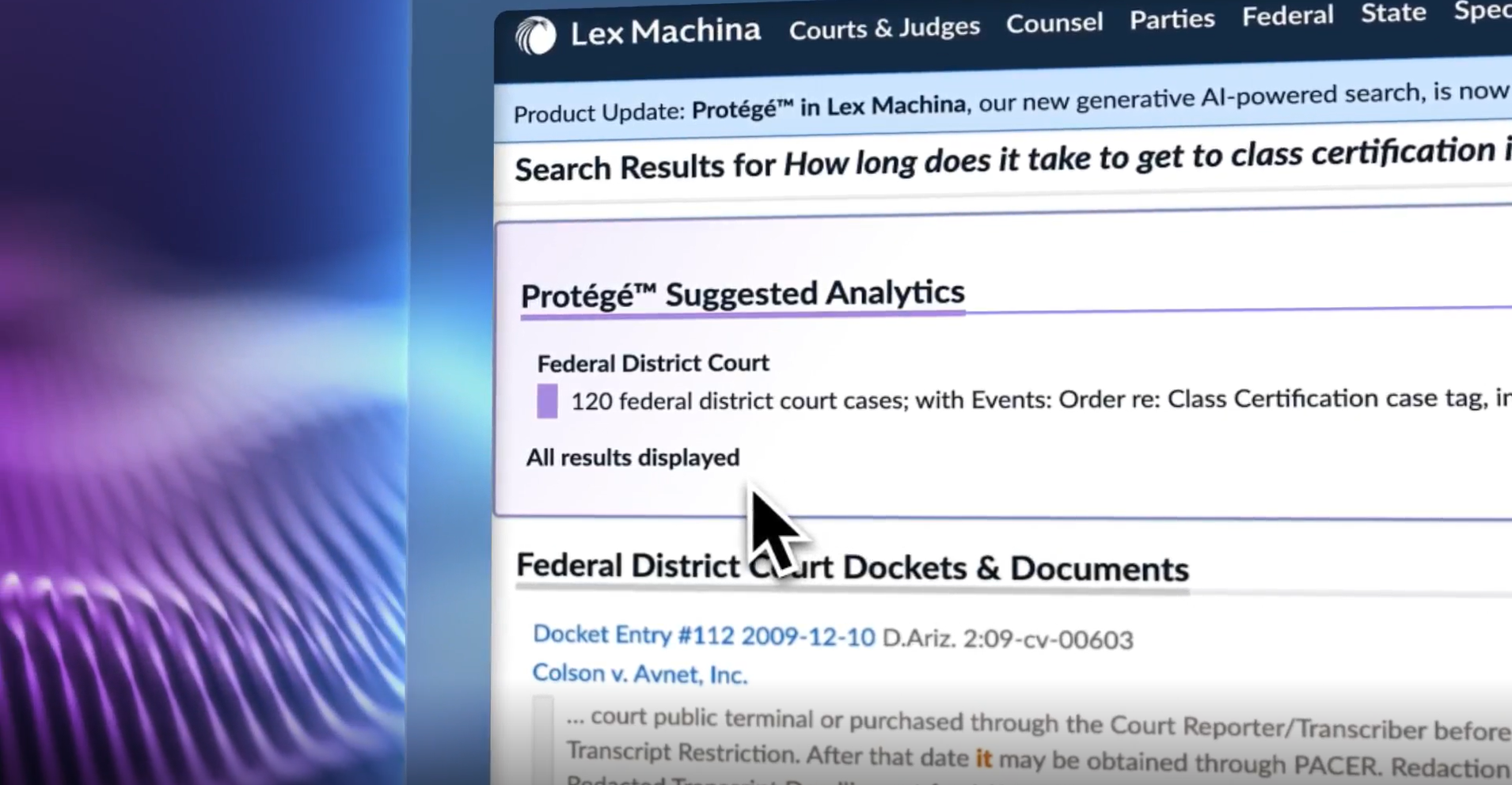
Extractive AI focuses on extracting specific information or insights from existing data sources, such as documents, images, or audio files. Extractive AI excels at information retrieval, data summarization, and precision in response. It uses natural language processing (NLP) to precisely identify and extract relevant text or data from lengthy or unstructured documents or datasets based on keywords or queries. It became widely used in the 1990s and 2000s due to advancements in machine learning and the increased availability of digital text. It is applied in many familiar consumer technologies such as search engines. Extractive AI is applied in many of LexisNexis’s solutions to search through vast, unstructured data and return precise, clear responses. For example, in the Ask a Question of Firm Content or Vault functionality, Protégé in Lexis+ AI leverages extractive AI—as well as other forms of AI discussed below—to retrieve relevant information in firm documents, DMS, or uploaded Vault documents.
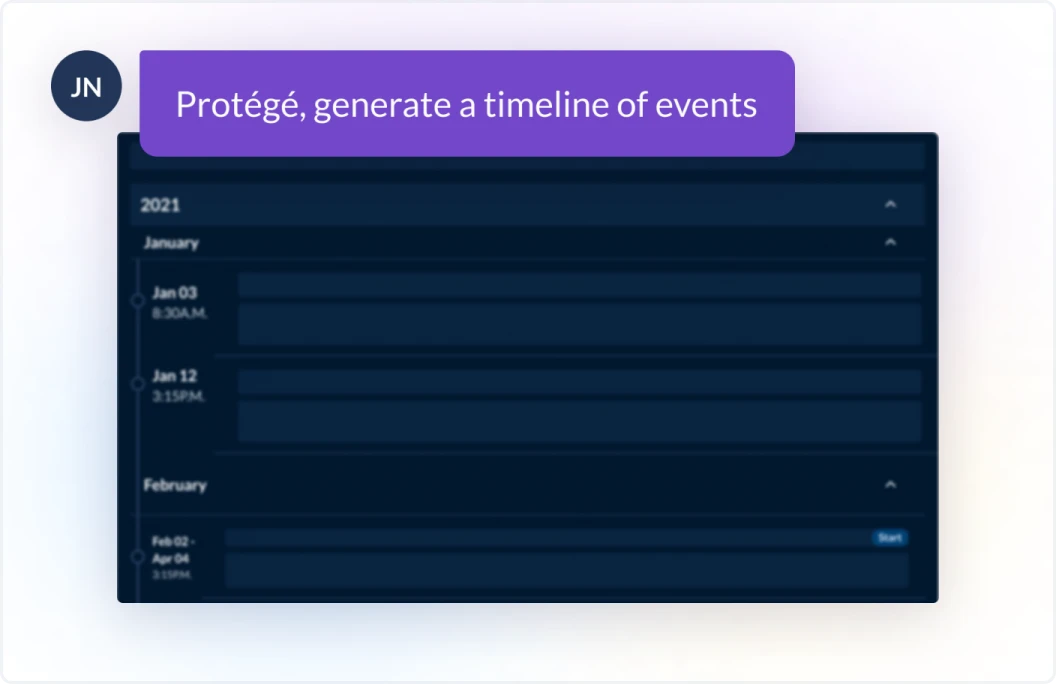
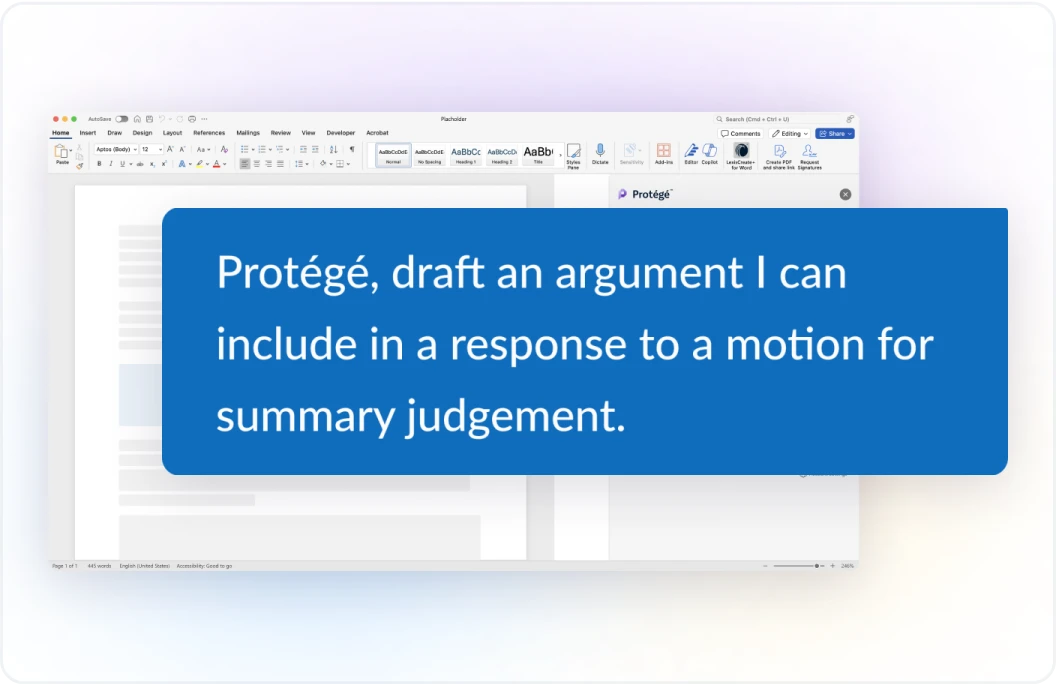
Generative AI specializes in creating new content, such as text, images, music, or code, by learning from patterns in existing data. Generative AI, also known as genAI, excels at content creation, data-driven pattern recognition and application, and creative versatility. While generative AI originated through applications machine learning in the 20th century, widespread use and consumer awareness occurred more recently due to major advancements in deep learning and large language models (LLMs). It powers tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and DALL-E, which use vast quantities of underlying data to generate high-quality text, images, and other content. LexisNexis applies generative AI in tools like Lexis+ AI and Nexis+ AI to offer an AI assistant experience which includes features like conversational search, document summarization, document drafting, and more. Among the company’s unique generative AI achievements are the management and minimization of hallucinations, which are inaccurately produced creation of false or misleading content. Protégé, which is the next generation of the AI assistant experience, applies generative AI to power most of its features that involve the production of text, including but not limited to Conversational Search, Generate a Timeline, and Full Document Drafting.
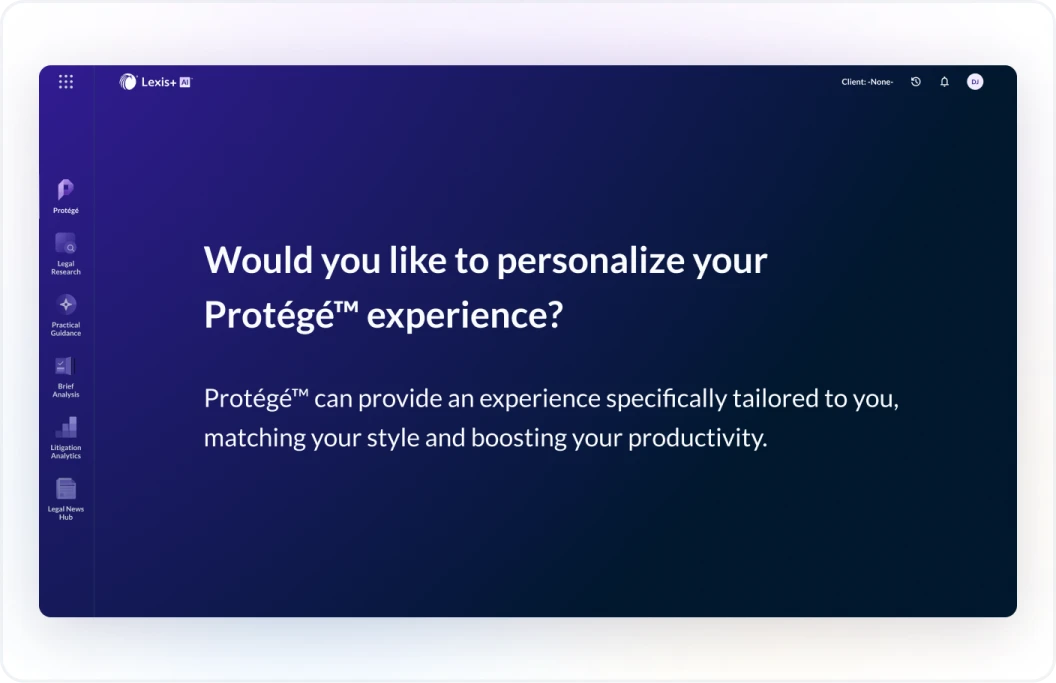
Agentic AI focuses on creating autonomous AI agents that can perform tasks, make decisions, and adapt based on real-time inputs. AI agents are software entities that can perform tasks autonomously by perceiving its environment, making decisions, and taking actions to achieve specific goals. Agentic AI excels at autonomous task execution, real-time adaptation, and workflow automation. Also, with its roots in the 20th century, agentic AI gained more widespread use in the 2010s and 2020s with the rise of machine learning, neural networks, and reinforcement learning. Agentic AI is applied in autonomous vehicles and intelligent AI assistants. LexisNexis applies agentic AI to power the Protégé personalization, proactive suggestion, and workflow automation features, including but not limited to Prompt Assistance, Full Document Drafting, and Analyze Transactional and Litigation Documents. Agentic AI is an area of continuous focus for LexisNexis and many other high technology companies and will be a cornerstone of many ongoing advancements in the information services industry.
It’s important to note that these forms of AI have been areas of scientific exploration for decades and already appear in technology that individuals use every day, such as Google Search, iPhones, and Microsoft Word. While individuals may not need to understand the full breadth and history of artificial intelligence for their daily work tasks, understanding the definitions and differences can be helpful to identifying assessing the right tools for their personal and professional use.